
Can You Do Glute Exercises Daily (3 Helpful Guidelines)
Can you do glute exercises daily? Many fitness enthusiasts wonder about the feasibility and benefits of incorporating daily glute workouts into their routine. Unlocking the secrets to a sculpted, toned posterior isn’t just a fitness trend—it’s a journey toward confidence, strength, and yes, a killer backside.
But the burning question remains: can you really embark on this journey every single day? Imagine waking up each morning with the promise of shaping those glutes to perfection, the allure of a daily routine promising progress with every rep. Let’s dive into the captivating world of glute exercises, where dedication meets determination and the quest for that coveted peach emoji-worthy physique knows no bounds.

Can You Do Glute Exercises Daily
Yes, you can do glute exercises daily, but it’s important to vary your routine and intensity to prevent overtraining and promote muscle growth effectively.
Benefits of Daily Glute Exercises
Engaging in glute exercises on a daily basis can yield various benefits. By targeting the gluteal muscles regularly, individuals aim to enhance strength, improve stability, and achieve a more toned appearance. Consistent exercise may also contribute to better posture and alleviate discomfort associated with prolonged sitting.
Considerations for Daily Workouts
While daily glute exercises can be beneficial, it’s crucial to approach them with caution. Overtraining specific muscle groups, including the glutes, may lead to fatigue, injury, or stagnation in progress. It’s advisable to incorporate rest days, alternate muscle groups, and vary exercise intensity to prevent burnout and ensure balanced development.
Diversifying Your Routine
To optimize results and minimize the risk of overuse injuries, individuals should diversify their glute exercise routine. Incorporating a mix of compound movements, isolation exercises, and plyometrics can target the gluteal muscles from various angles and challenge them in different ways. Additionally, integrating stretches and mobility drills can improve flexibility and range of motion.
Understanding Glute Exercises
Types of Glute Exercises
Compound exercises
Compound exercises are the cornerstone of effective strength training routines, emphasizing movements that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. These exercises, such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups, offer numerous benefits beyond isolated exercises by promoting functional strength, muscle coordination, and overall athleticism.
They recruit a greater number of muscles, leading to efficient workouts that maximize muscle growth and calorie burn. Additionally, compound exercises enhance stability and balance as they mimic real-world movements, making them invaluable for improving daily activities and athletic performance. Whether the goal is to build muscle, increase strength, or enhance overall fitness, incorporating compound exercises into a workout regimen is essential for achieving optimal results.
Isolation exercises
Isolation exercises are a fundamental component of strength training routines, targeting specific muscles or muscle groups in isolation from surrounding muscles. Unlike compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, isolation exercises focus on isolating a single muscle or joint, allowing for more precise muscle targeting and development.
These exercises typically involve movements that isolate a particular muscle group through controlled, repetitive motions. Common examples include bicep curls, tricep extensions, leg extensions, and calf raises. Incorporating isolation exercises into a workout regimen can help address muscle imbalances, improve muscle definition, and enhance overall muscular strength and endurance. However, they are often used in conjunction with compound exercises to ensure balanced muscle development and functional strength.
Targeted Muscles
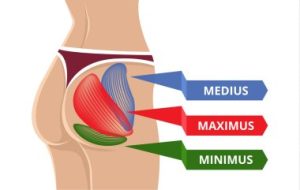
Gluteus maximus
The gluteus maximus, often referred to as the largest muscle in the human body, plays a critical role in movement and stability. Situated in the buttocks, it is responsible for extending the hip joint, as well as assisting in movements such as walking, running, and climbing. Not only does the gluteus maximus provide power and force during activities like sprinting and jumping, but it also aids in maintaining proper posture and pelvic alignment.
Additionally, its strength and activation are vital for injury prevention, particularly in the lower back and lower extremities. Regular exercises targeting the gluteus maximus, such as squats, lunges, and hip thrusts, are integral for overall lower body strength and functionality.
Gluteus medius and minimus
The gluteus medius and minimus are two essential muscles located in the buttocks region, playing crucial roles in stabilizing the pelvis and facilitating movements of the hip joint. The gluteus medius, situated on the outer surface of the pelvis, originates from the ilium and inserts onto the greater trochanter of the femur. It functions primarily in abduction of the hip, meaning it moves the leg away from the midline of the body.
Additionally, it assists in internal and external rotation of the thigh. Working in tandem with the medius, the gluteus minimus lies beneath it and shares similar functions, aiding in hip abduction and rotation. Both muscles contribute significantly to maintaining balance during activities like walking, running, and standing, while also providing stability to the pelvis during single-leg movements.
Dysfunction or weakness in these muscles can lead to various issues such as hip pain, instability, and altered gait patterns. Therefore, proper strengthening and conditioning of the gluteus medius and minimus are crucial for overall lower body function and injury prevention.
Benefits of Glute Exercises
Improved posture
Glute exercises offer a multitude of benefits, among which is improved posture. Strengthening the glute muscles helps support the pelvis and spine, aiding in maintaining proper alignment of the body. When the glutes are weak or underdeveloped, it can lead to compensatory movements and imbalances in other parts of the body, potentially causing poor posture.
By engaging in targeted glute exercises such as squats, lunges, and hip thrusts, individuals can enhance their stability and alignment, reducing the risk of postural issues and associated discomfort. Additionally, a strong and stable core, which is often achieved through glute exercises, further contributes to maintaining an upright and balanced posture.
Enhanced athletic performance
Glute exercises offer a plethora of benefits, among which enhanced athletic performance stands out prominently. The glutes, comprising the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, are pivotal muscles involved in various athletic movements such as running, jumping, and squatting. Strengthening these muscles through targeted exercises not only improves overall lower body strength but also aids in stability and power generation.
Enhanced glute strength leads to better propulsion during activities like sprinting and jumping, resulting in improved speed, agility, and explosiveness. Additionally, strong glutes contribute to better posture and reduce the risk of injuries by providing support to the lower back and hips. Incorporating glute exercises into a workout regimen can significantly enhance athletic performance across a range of sports and activities.
Prevention of injuries
Engaging in regular glute exercises offers a myriad of benefits, foremost among them being the prevention of injuries. Strong glutes play a crucial role in stabilizing the pelvis and supporting proper alignment of the spine during various movements, such as squatting, lunging, and jumping. By strengthening these muscles, individuals can reduce the risk of common injuries, including strains, sprains, and even lower back pain.
Aesthetic benefits
Glute exercises offer a multitude of aesthetic benefits that go beyond just building a shapely posterior. Engaging in targeted glute workouts can lead to a firmer, more lifted appearance, enhancing the overall contours of the body. Strengthening the glute muscles not only improves posture but also contributes to a more balanced physique, reducing the likelihood of muscular imbalances and potential injuries.
Additionally, a well-developed gluteal region can create a visually appealing silhouette, boosting confidence and self-esteem. As these muscles are among the largest in the body, focusing on their enhancement can also aid in burning calories and sculpting a leaner physique, further enhancing one’s aesthetic appeal.
Frequency of Glute Exercises
Rest and recovery
Importance of rest days for muscle repair and growth
Rest days are an indispensable component of any effective fitness regimen, especially for individuals seeking muscle repair and growth. While intense workouts stimulate muscle fibers, it’s during periods of rest that these fibers undergo repair and growth. Rest days allow muscles to recover from the stress of exercise, minimizing the risk of overtraining and injury.
Additionally, adequate rest promotes hormonal balance, including the release of growth hormone and testosterone, which are crucial for muscle development. Neglecting rest days can lead to diminished performance, increased susceptibility to injury, and plateauing in muscle growth. Therefore, incorporating regular rest days into a training routine is essential for optimizing muscle repair and fostering long-term strength and development.
Impact of overtraining on muscle development
Overtraining can significantly hinder muscle development, contrary to the belief that more training leads to better results. When the body is pushed beyond its limits without adequate rest and recovery, it can lead to chronic fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury. Muscles need time to repair and grow stronger after intense workouts, but overtraining disrupts this process, leading to muscle breakdown rather than growth.
Moreover, overtraining can elevate levels of stress hormones such as cortisol, which can further inhibit muscle growth and even promote muscle loss. In essence, while pushing one’s limits is essential for progress, balance is key to optimizing muscle development and avoiding the detrimental effects of overtraining.
Frequency guidelines
General recommendations for strength training frequency
General recommendations for strength training frequency typically suggest engaging in strength training activities at least two to three times per week, with a rest day in between sessions to allow for muscle recovery and growth. This frequency allows for sufficient stimulus to maintain and improve muscular strength and endurance while minimizing the risk of overtraining and injury.
Consideration of individual factors (fitness level, recovery capacity)
Tailoring frequency to individual factors such as fitness level and recovery capacity is crucial. Beginners may require more rest between sessions, while advanced individuals might benefit from higher training frequencies. Specific frequency may vary based on individual goals, fitness levels, and training intensity. Additionally, incorporating a variety of exercises targeting major muscle groups throughout the week can help promote balanced strength development and overall fitness.
Research insights
Studies on muscle protein synthesis and recovery time
Research indicates that muscle protein synthesis peaks within 24-48 hours post-exercise and gradually declines thereafter. This suggests that allowing adequate recovery time between sessions is essential for maximizing muscle growth.
Optimal frequency for muscle growth and strength gains
Studies have shown that a frequency of 2-3 sessions per week is optimal for promoting muscle growth and strength gains. This balanced approach ensures adequate stimulus for adaptation while allowing sufficient recovery time for optimal results.
Factors to Consider
Intensity of workouts
High-intensity vs. low-intensity exercises
When considering workout intensity, it’s vital to weigh the benefits and risks of high-intensity versus low-intensity exercises. Intensity levels dictate the exertion required and the impact on the body’s systems. High-intensity workouts involve maximal effort, while low-intensity exercises are less demanding and often focus on endurance or recovery. It’s crucial to assess your fitness goals, current physical condition, and overall health before determining the suitable intensity for your workouts.
Variation in volume and resistance
The variation in workout volume and resistance plays a significant role in achieving desired fitness outcomes. Volume refers to the total amount of work performed, including sets, reps, and weight lifted, while resistance pertains to the level of challenge provided by the weights or resistance bands. Balancing volume and resistance ensures progressive overload, which is essential for muscle growth and strength gains. By adjusting these factors appropriately, individuals can tailor their workouts to match their specific goals and capabilities.
Exercise selection
Balancing compound and isolation exercises
Effective exercise selection involves striking a balance between compound and isolation exercises. Compound exercises engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, such as squats or deadlifts, while isolation exercises target specific muscles, like bicep curls or leg extensions. Incorporating both types of exercises into a workout routine ensures comprehensive muscle development and functional strength. It’s important to prioritize compound movements for overall strength and stability while incorporating isolation exercises to address specific weaknesses or aesthetic goals.
Avoiding overloading specific muscle groups
Overloading specific muscle groups can lead to imbalances, overuse injuries, and hindered progress. It’s essential to distribute workload evenly across different muscle groups to prevent overtraining and ensure balanced development. Incorporating a variety of exercises that target complementary muscle groups helps maintain symmetry and reduces the risk of injury. Listening to your body’s signals and adjusting your workout routine accordingly can help prevent overloading specific muscles and promote overall fitness and health.

Individual differences
Fitness level and experience
Individual differences in fitness level and experience significantly impact workout effectiveness and safety. Beginners may need to start with simpler exercises and lighter weights to build a foundation of strength and technique, while experienced individuals can handle more advanced movements and heavier loads. Understanding your fitness level and gradually progressing ensures sustainable results and minimizes the risk of injury. Tailoring workouts to individual capabilities fosters long-term adherence and success.
Age and hormonal factors
Age and hormonal factors influence exercise tolerance, recovery, and adaptation. As individuals age, hormonal fluctuations and changes in muscle mass, bone density, and metabolism affect exercise performance and recovery rates. It’s essential to adjust workout intensity, duration, and recovery strategies according to age-related considerations. Moreover, hormonal imbalances, such as those related to thyroid function or menopause, may impact energy levels, mood, and body composition, necessitating modifications to exercise routines and lifestyle habits.
Injury history and susceptibility
Prior injuries and susceptibility to specific types of injuries should be carefully considered when designing a workout program. Past injuries may require modifications to exercise selection, technique, or intensity to prevent exacerbation or recurrence. Additionally, individuals with underlying musculoskeletal issues or joint instability may need to focus on corrective exercises and injury prevention strategies. Consulting with a healthcare professional or qualified fitness trainer can help tailor a workout plan that accommodates injury history and minimizes the risk of further harm, ensuring safe and effective progress.
Pros and Cons of Daily Glute Exercises
Pros of Daily Glute Exercises
Increased Muscle Stimulation
Engaging in daily glute exercises offers a multitude of benefits, with increased muscle stimulation being one of the primary advantages. Consistent activation of the gluteal muscles through exercises like squats, lunges, and hip thrusts not only strengthens these muscles but also enhances their responsiveness and endurance. This heightened stimulation leads to greater muscle growth and definition over time, contributing to a firmer, more sculpted posterior.
Accelerated Muscle Development
Accelerated muscle development refers to the process of rapidly increasing muscle size, strength, and definition through targeted training methods, proper nutrition, and adequate rest. This approach typically involves high-intensity workouts, progressive overload, and strategic recovery techniques. By challenging the muscles with heavier weights and varying exercises, individuals can stimulate muscle growth more efficiently.
Enhanced Muscle Endurance
Enhanced muscle endurance refers to the increased capacity of muscles to sustain repeated contractions over an extended period without fatigue. This adaptation is typically achieved through consistent training and targeted exercises that stress the muscles beyond their usual limits. Endurance training stimulates physiological changes within muscle fibers, such as improved oxygen utilization, increased mitochondrial density, and enhanced buffering capacity against lactic acid buildup.
These adaptations enable muscles to perform for longer durations without experiencing exhaustion, allowing individuals to engage in activities like long-distance running, cycling, or prolonged resistance training with greater efficiency and resilience. Enhanced muscle endurance not only enhances physical performance but also promotes overall health and well-being by improving cardiovascular function and metabolic efficiency.

Cons of Daily Glute Exercises
Risk of Overtraining and Injury
One of the primary drawbacks of engaging in daily glute exercises is the heightened risk of overtraining and injury. While consistent exercise is crucial for muscle development, pushing the body too hard without adequate rest and recovery can lead to overuse injuries such as strains, sprains, or even more severe conditions like muscle tears.
The glute muscles, being large and powerful, require sufficient time to repair and rebuild after intense workouts. Constantly subjecting them to daily stress without adequate recovery periods can result in diminished performance, chronic pain, and potentially long-term damage. It’s essential to strike a balance between exercise intensity, frequency, and recovery to promote optimal muscle growth and minimize the risk of injury.
Insufficient Recovery Time
The other most prominent cons of engaging in daily glute exercises is the potential for insufficient recovery time. While consistent training is vital for muscle growth and strength development, overworking the glute muscles without adequate rest can lead to fatigue, strain, and even injury. Muscles need time to repair and rebuild after intense workouts, and without proper recovery periods, the risk of overuse injuries such as strains or tears increases significantly. Continuous stress on the glute muscles without allowing them sufficient time to recover can hinder progress and potentially impede overall performance in the long run. Thus, incorporating rest days into a workout routine is crucial for optimizing results and minimizing the risk of overtraining.
Potential Plateauing
One notable drawback of engaging in daily glute exercises is the risk of plateauing. Over time, the muscles can adapt to the repetitive routine, leading to diminished returns in terms of strength and growth. Without sufficient variation in exercises or intensity, the glutes may cease to respond as effectively, hindering progress and potentially stalling overall development. Moreover, constant strain on the muscles without ample rest can increase the likelihood of overuse injuries, further impeding long-term fitness goals. Therefore, it’s crucial to incorporate adequate rest days and diversify workout routines to mitigate the risk of plateauing and optimize muscular growth and strength.
Strategies for Safe and Effective Glute Training
Periodization
Incorporating phases of high and low training frequency
Optimize glute training by alternating between periods of intense workouts and lighter sessions. This approach prevents plateauing and fosters continuous progress.
Deloading weeks to allow for recovery
Integrate recovery weeks into your routine to prevent overtraining and injury. These breaks facilitate muscle repair and adaptation, enhancing long-term performance.
Active recovery methods
Incorporating mobility exercises and stretching
Enhance flexibility and range of motion with targeted stretches and mobility drills. These activities improve blood flow and reduce the risk of muscle tightness or imbalances.
Utilizing foam rolling and massage therapy
Alleviate muscle tension and soreness through foam rolling and professional massages. These techniques aid in recovery, promoting faster muscle repair and relaxation.
Listening to the body
Paying attention to signs of fatigue, soreness, and injury
Stay attuned to your body’s signals during glute training. Address fatigue, soreness, or discomfort promptly to prevent potential injuries and setbacks.
Adjusting workout frequency and intensity accordingly
Modify your training regimen based on your body’s response and recovery needs. This adaptive approach ensures sustainable progress while minimizing the risk of overtraining.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Can You Do Glute Exercises Daily
Q1. Is it safe to do glute exercises every day?
A. While it’s generally safe to exercise daily, focusing solely on glutes every day may lead to overuse injuries. It’s advisable to incorporate rest days to allow muscle recovery and growth.
Q2. Can I see faster results by exercising my glutes daily?
A. Results from glute exercises depend on various factors like genetics, diet, and overall workout routine. Overtraining may hinder progress rather than accelerate it. Consistency and proper rest are key for optimal results.
Q3. Will doing glute exercises every day lead to muscle imbalances?
A. Yes, concentrating solely on one muscle group can create imbalances, potentially leading to issues like lower back pain. Incorporate a balanced workout routine targeting different muscle groups to avoid imbalances.
Q4. Are there specific glute exercises suitable for daily practice?
A. Some glute exercises, like bodyweight squats, lunges, and bridges, are generally safe for daily practice. However, it’s essential to vary the intensity and focus on proper form to prevent injury.
Q5. How do I know if I’m overtraining my glutes?
A. Signs of overtraining include persistent muscle soreness, decreased performance, fatigue, and lack of progress. Listen to your body, and if you experience these symptoms, consider incorporating rest days or reducing exercise frequency.
Q6. Can beginners do glute exercises every day?
A. Beginners should start with a less frequent schedule to allow their muscles to adapt and recover. Gradually increase frequency as strength and endurance improve, but always prioritize proper form and recovery.
Q7. Should I incorporate rest days even if I’m doing glute exercises daily?
A. Yes, rest days are crucial for muscle repair and growth. Consider scheduling rest days or incorporating light activities like stretching or walking to promote recovery and prevent overuse injuries.
Q8. Can I combine different types of glute exercises into my daily routine?
A. Yes, diversifying your routine with various glute exercises can prevent boredom and target different muscle fibers. However, ensure you’re not overloading specific muscles and allow for adequate recovery between workouts.
Q9. How long should my daily glute workout be?
A. The duration of your glute workout depends on factors like fitness level, intensity, and exercise selection. Aim for at least 15-30 minutes of focused glute exercises, adjusting based on your goals and personal capacity.
Q10. Should I consult a fitness professional before starting daily glute exercises?
A. It’s always wise to seek advice from a qualified fitness trainer or physical therapist, especially if you’re new to exercise or have any pre-existing conditions. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure your workout routine is safe and effective.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while it may seem tempting to perform glute exercises every day in pursuit of quicker results, it’s crucial to prioritize balance and recovery in any fitness routine. Overtraining the glutes without adequate rest can lead to diminished gains, increased risk of injury, and overall fatigue. Incorporating rest days into your regimen allows muscles to repair and grow stronger, ultimately optimizing performance and preventing burnout. Therefore, while consistency is key, it’s equally important to listen to your body, vary your workouts, and give your glutes the time they need to recover for long-term progress and overall well-being.