
Starting Out Exercising With Asthma (3 Best Exercises)
Starting out exercising with asthma requires careful planning and consultation with a healthcare professional to develop a safe and effective workout routine tailored to your individual respiratory needs. In the rhythmic dance of life, our breath orchestrates the symphony of vitality. Yet, for those who grapple with the capricious companion known as asthma, each inhalation becomes a delicate negotiation between ambition and respiration.
Asthma, the elusive maestro of the respiratory system, wields the power to conduct an unconventional symphony within the realm of fitness. It transforms the mundane act of breathing into a nuanced ballet, demanding a delicate choreography that intertwines with the pulsating cadence of a fitness routine.
As the wheezing overture commences, a unique question emerges: How does asthma, this enigmatic soloist of the lungs, influence the harmonious pursuit of physical well-being? In this intricate pas de deux between breath and exertion, the answer unfolds, revealing a narrative of resilience, adaptation, and the boundless spirit of those who dare to dance in the face of adversity.

Starting Out Exercising With Asthma
Understanding the Impact of Asthma on Fitness Routines
Living with asthma can significantly impact your fitness routine, requiring careful consideration and adaptation to ensure a safe and effective exercise regimen. Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition, can influence how individuals approach their fitness routines. This condition, characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, poses unique challenges that necessitate a tailored approach to exercise.
Navigating Exercise with Asthma
Navigating exercise with asthma requires a personalized approach that blends physical activity with respiratory considerations. Begin by consulting a healthcare professional to understand your specific asthma triggers and limitations. Choose exercises that accommodate your condition, favoring activities like swimming, walking, or yoga, which are gentler on the respiratory system.
Gradually increase intensity and duration, always listening to your body. Keep rescue medication handy, warm up thoroughly, and prioritize proper breathing techniques. By adopting a cautious yet proactive mindset, individuals can navigate exercise with asthma successfully, unlocking the benefits of an active lifestyle while managing their respiratory health effectively.
Adaptations and Considerations
Embarking on an exercise regimen with asthma necessitates a thoughtful approach centered around adaptation and consideration. It’s crucial to adapt workout routines to align with individual respiratory capacities, focusing on gradual progress and avoiding overly strenuous activities.
Strategies for Success
Strategies for success in starting out exercising with asthma involve gradually increasing intensity, incorporating warm-up and cool-down routines, and choosing asthma-friendly activities like swimming or walking. Additionally, consistent communication with healthcare professionals ensures a personalized approach, promoting a sustainable and successful fitness journey despite asthma challenges.
Understanding Asthma and its Impact on Fitness
Respiratory System Overview
The respiratory system, often termed the lungs and airways, plays a vital role in our body’s oxygen exchange. Comprising the trachea, bronchi, and alveoli, it facilitates breathing. Understanding this intricate system is crucial to grasp how asthma impacts fitness.
Asthma Pathophysiology
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. This inflammation leads to increased sensitivity, making individuals prone to asthma attacks triggered by various factors. Recognizing the underlying pathophysiology is fundamental to managing asthma’s impact on fitness.
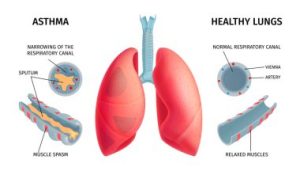
Exercise-Induced Asthma (EIA)
Exercise-Induced Asthma (EIA) is a specific form of asthma triggered by physical exertion. During exercise, individuals with EIA may experience wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Addressing the nuances of EIA is essential to tailor fitness routines for those susceptible to exercise-induced symptoms.
Factors Affecting Asthma and Exercise Tolerance
Various factors influence asthma and exercise tolerance. Environmental factors like air quality, allergens, and temperature, coupled with individual triggers, can significantly impact one’s ability to engage in physical activity. Recognizing and managing these factors is key to optimizing exercise routines for individuals with asthma.
Benefits of Exercise for Asthma Patients
Improved Respiratory Function
Regular exercise significantly enhances respiratory function for asthma patients. Engaging in physical activity helps expand lung capacity, allowing individuals to breathe more efficiently. This can lead to decreased breathlessness and improved airflow, providing asthma patients with a greater sense of ease during daily activities. Incorporating exercises like deep breathing and aerobic workouts can contribute to increased lung efficiency, a crucial aspect of managing asthma symptoms.
Strengthening Respiratory Muscles
Exercise plays a pivotal role in strengthening the respiratory muscles, offering added support for asthma patients. Targeted workouts, such as diaphragmatic breathing exercises and inspiratory muscle training, can fortify the muscles involved in the breathing process. This enhanced muscular strength contributes to better respiratory performance, reducing the strain on airways and aiding in the overall management of asthma symptoms.
Enhanced Cardiovascular Health
Regular physical activity promotes cardiovascular health, benefiting asthma patients by improving circulation and heart function. Cardio exercises like brisk walking or cycling enhance heart and lung efficiency, optimizing oxygen delivery throughout the body. This cardiovascular improvement not only supports overall health but also contributes to better endurance for individuals with asthma, enabling them to engage in daily activities with reduced risk of triggering symptoms.
Weight Management and Asthma Control
Exercise aids in weight management, a critical factor in asthma control. Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate the strain on the respiratory system, reducing the likelihood of asthma exacerbations. Additionally, regular physical activity helps control inflammation, a common trigger for asthma symptoms. Combining exercise with a balanced diet contributes to overall well-being, fostering a holistic approach to asthma management.
Psychological Benefits
Beyond the physical advantages, exercise provides essential psychological benefits for asthma patients. Regular activity contributes to stress reduction, anxiety management, and improved mood—all of which are crucial aspects of holistic asthma care. Engaging in enjoyable physical activities, such as yoga or nature walks, can enhance mental well-being, creating a positive impact on the overall quality of life for individuals managing asthma.

Designing a Fitness Routine for Asthma Patients
Medical Clearance and Consultation
Ensuring a safe start to designing a fitness routine for asthma patients begins with obtaining medical clearance and consulting with a healthcare professional. Prioritize discussions on individual health conditions, recent asthma symptoms, and any medications being taken. This step is crucial for crafting a tailored fitness plan that aligns with the patient’s medical history and current health status. Obtaining a doctor’s approval is a fundamental safeguard for those navigating asthma challenges, providing confidence and reassurance.
Choosing Asthma-Friendly Activities
Optimal fitness routines for asthma patients focus on activities that promote cardiovascular health without triggering respiratory distress. Consider low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, or cycling, which minimize strain on the respiratory system. Tailoring the routine to individual preferences and comfort levels is essential, fostering adherence and enjoyment. These asthma-friendly activities provide a foundation for a sustainable and beneficial fitness journey.
Warm-Up and Cool-Down Strategies
Prioritizing warm-up and cool-down routines is pivotal for asthma patients to prepare and recover effectively. Gentle exercises like stretching or slow-paced walking gradually ease the body into activity, reducing the risk of sudden asthma exacerbations. Incorporating these strategies ensures that the respiratory system adapts smoothly to increased physical demands, enhancing overall exercise tolerance and minimizing post-exercise discomfort.
Gradual Progression and Monitoring
A key principle in designing fitness routines for asthma patients is the emphasis on gradual progression and continuous monitoring. Start with manageable intensity levels and gradually increase as the patient’s fitness improves. Regular monitoring, including tracking asthma symptoms and exercise performance, enables timely adjustments and ensures a safe and sustainable progression towards fitness goals.
Incorporating Breathing Techniques
Integrating specific breathing techniques is vital for asthma patients during exercise. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing enhance respiratory efficiency, promoting better oxygen exchange and reducing the likelihood of asthma-related discomfort. Educating patients on these techniques empowers them to proactively manage their breathing, fostering a sense of control during physical activity.
Avoiding Triggers and Environmental Considerations
Mitigating potential triggers is central to a successful asthma-friendly fitness routine. Identify and avoid environmental factors that may exacerbate symptoms, such as pollution or allergens. Choosing indoor activities during high pollen seasons and monitoring air quality supports a comfortable exercise environment. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of asthma episodes, ensuring a consistent and enjoyable fitness experience.
Asthma-Friendly Exercises
Aerobic Exercises
Walking
Asthma-friendly exercises often include low-impact options like walking, which promotes cardiovascular health without triggering respiratory distress. Enjoy a brisk stroll in nature, ensuring a gentle pace that suits your breathing capacity.
Swimming
Dive into the benefits of swimming, a buoyant exercise that enhances lung capacity and builds endurance. The soothing nature of water provides a comfortable environment for asthmatics, promoting a holistic approach to fitness.
Cycling
Opt for cycling as a respiratory-friendly aerobic activity, engaging in smooth, rhythmic movements. A bike ride not only improves cardiovascular fitness but also minimizes the risk of asthma exacerbation associated with high-impact exercises.
Low-Impact Aerobics
Embrace low-impact aerobics tailored for individuals with asthma. These exercises, often featuring controlled movements, help elevate heart rate gradually, allowing for optimal oxygen intake without overwhelming the respiratory system.

Strength Training
Focus on Core and Respiratory Muscles
Strengthening exercises need not be daunting for asthmatics. Targeting core and respiratory muscles through controlled movements can enhance overall lung function and respiratory efficiency.
Light to Moderate Resistance
Choose strength training exercises with light to moderate resistance to avoid undue strain on the respiratory system. This approach ensures a balanced workout without compromising breathing patterns.
Flexibility and Stretching Exercises
Yoga
Integrate yoga into your fitness routine for a holistic approach to asthma-friendly exercises. Yoga emphasizes controlled breathing, enhances flexibility, and reduces stress, creating an ideal synergy for individuals managing asthma.
Pilates
Incorporate Pilates, a low-impact exercise method, into your regimen to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. The controlled movements and emphasis on breath awareness make Pilates a suitable choice for those with asthma.

Special Considerations for Asthma and Exercise
Medication Management
Effective asthma management during exercise hinges on proper medication use. Inhalers, bronchodilators, and anti-inflammatory drugs play a pivotal role in preventing exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Employing prescribed medications ensures optimal airway function, allowing individuals to engage in physical activities without compromising respiratory health.
Timing of Medication and Exercise
Strategic timing of asthma medication and exercise is crucial. Pre-exercise bronchodilator use, approximately 15-30 minutes before activity, helps open airways and mitigate exercise-induced symptoms. Consistent adherence to prescribed medication schedules ensures that individuals can fully enjoy the benefits of physical activity without undue respiratory distress.
Emergency Action Plan
Having a well-defined emergency action plan is paramount for individuals with asthma engaging in exercise. This plan, typically crafted in consultation with healthcare professionals, outlines specific steps to take in case of an asthma attack during physical activity. Immediate access to rescue medications and clear communication of the action plan to relevant parties contribute to effective crisis management.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Being attuned to warning signs is essential for individuals with asthma during exercise. Recognizing subtle changes in breathing patterns, increased coughing, or chest tightness prompts early intervention. Heightened awareness empowers individuals to address potential exacerbations swiftly, minimizing the impact on their exercise routine.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring and proactive adjustments in asthma management are key to maintaining optimal respiratory health during exercise. Tracking symptoms, peak flow measurements, and consulting healthcare providers for periodic reviews allow for personalized adjustments to the treatment plan. This iterative process ensures ongoing suitability of the management strategy.
Overcoming Barriers to Exercise
Overcoming Fear and Anxiety
Overcoming fear and anxiety associated with exercise is crucial for building a sustainable fitness routine. Many individuals express trepidation about starting a new workout regimen, fearing judgment, failure, or physical discomfort. Addressing these concerns requires a gradual approach, allowing individuals to acclimate at their own pace. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and positive self-talk can help manage anxiety during workouts, fostering a sense of empowerment and achievement.
Boosting Motivation
Lack of motivation often hinders consistent exercise habits. Individuals frequently cite struggles in maintaining enthusiasm and commitment. To overcome this, setting realistic and specific goals provides a clear roadmap for progress. Incorporating enjoyable activities and variety into the fitness routine prevents monotony and sparks interest. Utilizing motivational tools, such as fitness apps and tracking progress, serves as a constant reminder of achievements, reinforcing the drive to stay active.
Conquering Environmental Factors
Environmental barriers, such as time constraints and lack of access to fitness facilities, can impede regular exercise. Emphasizing the importance of adaptable, time-efficient workouts that can be done at home or in local surroundings is essential. Leveraging technology for virtual classes or utilizing outdoor spaces promotes flexibility. Encouraging the incorporation of physical activity into daily routines, like taking the stairs or walking during breaks, helps overcome environmental obstacles.
Fostering Social Support and Community Engagement
Establishing a supportive social network significantly contributes to overcoming exercise barriers. Building connections with like-minded individuals creates a sense of accountability and encouragement. Joining fitness communities, either in person or online, provides a platform for shared experiences and tips. Engaging in group activities, whether virtual or local, enhances motivation and fosters a sense of belonging, making the fitness journey more enjoyable and sustainable.
Future Research and Developments
Advances in Asthma Treatment and Exercise
In the realm of asthma research, breakthroughs in treatment and exercise interventions are gaining prominence. Cutting-edge medications, like bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory drugs, are revolutionizing asthma management. Concurrently, exercise programs tailored for asthmatics are seeing significant progress, offering hope for improved lung function.
This symbiotic relationship between pharmaceutical innovations and exercise regimens is reshaping the narrative of asthma care. Individuals often seek information on “latest asthma medications” and “exercise for asthma improvement,” reflecting a growing interest in holistic approaches to managing this chronic condition.
Technology and Asthma Management
Leveraging technology can significantly enhance asthma management when embarking on an exercise routine. Mobile apps and wearable devices equipped with health monitoring features enable individuals to track respiratory parameters, such as lung function and oxygen saturation, in real-time.
This data empowers users to make informed decisions about their exercise intensity and duration. Additionally, online platforms provide access to virtual exercise programs tailored to asthma sufferers, offering guidance and support from the comfort of home. Integrating technology into the journey of starting out exercising with asthma not only facilitates personalized monitoring but also fosters a proactive and informed approach to achieving fitness goals while managing respiratory health.

Community Programs and Support
Community programs play a crucial role in supporting individuals as they embark on exercising with asthma. These initiatives provide a platform for shared experiences, knowledge exchange, and encouragement among those facing similar challenges. From group fitness classes designed with asthma-friendly modifications to informative workshops led by healthcare professionals, community programs create a supportive environment.
Moreover, access to resources such as online forums and local support groups empowers individuals with asthma to navigate their fitness journey, fostering a sense of camaraderie and motivation in the pursuit of a healthier, active lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Starting Out Exercising With Asthma
Q1: Can individuals with asthma engage in regular fitness routines?
A: Yes, individuals with asthma can participate in fitness routines, but it’s essential to tailor the exercises to their condition and consult with a healthcare professional.
Q2: How does asthma affect exercise tolerance?
A: Asthma can vary in severity, impacting exercise tolerance differently for each person. Some may experience shortness of breath, chest tightness, or coughing during physical activity.
Q3: Are there specific exercises recommended for people with asthma?
A: Generally, low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are well-tolerated. However, the choice of exercise should be individualized, considering the person’s specific asthma triggers and symptoms.
Q4: Can intense workouts trigger asthma symptoms?
A: Yes, high-intensity exercises may trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals. It’s crucial to gradually increase intensity and monitor how the body responds while being prepared to adjust the routine accordingly.
Q5: Should individuals with asthma avoid certain types of exercises?
A: It depends on the individual. Some may need to avoid exercises in cold, dry air, while others may need to steer clear of activities that involve prolonged, intense exertion. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine suitable exercises.
Q6: How can individuals with asthma prepare for a workout?
A: Pre-workout preparations include proper warm-ups, using prescribed inhalers as recommended by a healthcare professional, and understanding personal asthma triggers to minimize potential risks during exercise.
Q7: Is it safe to exercise during an asthma attack?
A: No, exercising during an asthma attack is not advisable. Individuals should follow their asthma action plan, which may involve using a rescue inhaler and seeking medical attention if necessary.
Q8: Can consistent exercise help manage asthma symptoms?
A: Yes, regular physical activity can improve lung function and overall cardiovascular health, potentially aiding in better asthma management. However, it’s crucial to strike a balance and avoid overexertion.
Q9: Are there specific precautions for exercising in different environments for people with asthma?
A: Yes, individuals with asthma should be cautious in extreme temperatures, high humidity, or polluted environments. Adjustments to the workout routine may be necessary to accommodate these factors.
Q10: How can fitness trainers adapt routines for clients with asthma?
A: Fitness trainers should be aware of their clients’ asthma conditions, encourage open communication, and modify exercises as needed. Understanding individual triggers and limitations is key to creating a safe and effective fitness plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, embarking on an exercise journey with asthma demands a thoughtful approach that prioritizes both fitness goals and respiratory well-being. By consulting with healthcare professionals, customizing workout routines, and maintaining open communication, individuals can overcome the challenges associated with asthma and cultivate a sustainable and health-focused exercise regimen.
Remember, with the right guidance and a commitment to gradual progress, exercising with asthma can not only enhance physical fitness but also contribute to overall respiratory health and improved quality of life.